JVM runtime data area
Runtime data is living in execution of application.
Some of data area are JVM-wise, means they create upon JVM startup and destroy when JVM shutdown.
Other data are thread specific, means their lifecycle is binded with thread lifecyclej
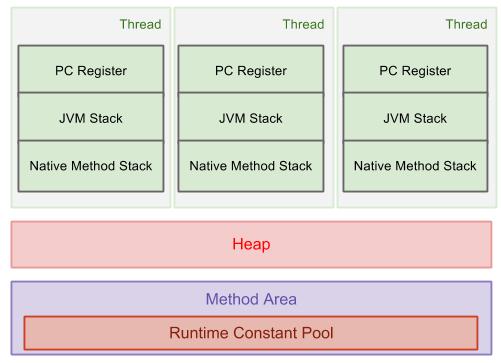
PC register(thread)
Each JVM thread has its own pc.
- The value will be the
address of JVM instruction+return addressof currently thread undefinedif the current method isnative
JVM stack(thread)
Each thread has its own stack.
Similar to the stack in C.
Does not have to be contiguous.
StackOverflowErrorif wants to have larger stack than permitted, larger in turns of the number frameOutOfMemoryErrorif wants to have more memory space than permitted
Heap
Heap is shared amongst all JVM threads.
Heap storage is managed by GC.
Heap can be fixed, expandable and shrinkable.
The memory does not need to be contiguous.
OutOfMemoryErrorif wants to have more memory space than permitted
Method area
Shared amongst all JVM threads
It is the text segement in ASM.
Can be fixed, expandable and shrinkable.
The memory does not need to be contiguous.
This area does not have to GC
OutOfMemoryErrorif wants to have more memory space than permitted
Contains class structure:
- runtime constant pool
- field data
- method data
- method code & constructor
- static block/method
native method stack(thread)
A C stack will be created for all native method
Allocated per thread.
Can be fixed, expandable and shrinkable.
StackOverflowErrorif wants to have larger stack than permitted, larger in turns of the number frameOutOfMemoryErrorif wants to have more memory space than permitted